Bradycardia: Slow Heart Rate
Quick Facts
- Bradycardia is a heart rate that’s too slow, usually less than 60 beats per minute.
- The most common type is sinus bradycardia.
- There are many causes of bradycardia. Treatment can depend on the cause.

ECG strip showing a normal heartbeat
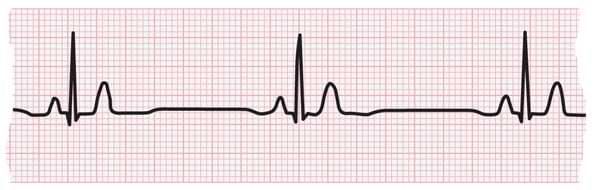
ECG strip showing bradycardia
Bradycardia is a heart rate that’s too slow. A normal average heart rate is 60-100 beats per minute. What’s considered too slow can depend on your age and physical condition. Elderly people, for example, are more prone to bradycardia.
An adult resting heart rate of fewer than 60 beats per minute (BPM) qualifies as bradycardia.
There are exceptions. Your heart rate may fall below 60 BPM during sleep. Athletes and physically active adults can sometimes have a resting heart rate less than 60 BPM.
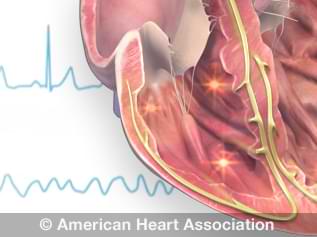
The most common type of bradycardia is sinus bradycardia. This is when the slowed rhythm comes from the sinus node of the heart.
View an animation of bradycardia.
What causes bradycardia?
Causes of bradycardia include:
- Problems with the sinus node, the heart’s natural pacemaker
- Problems with the AV node, the electrical area between the atria and ventricles, also known as heart block
- Metabolic problems such as low thyroid (hypothyroidism)
- Damage to the heart from aging, heart disease or heart attack
- Certain heart medications
- Congenital heart defects (present at birth)
- Infection of heart tissue, known as myocarditis
- Complications from heart surgery
- Chemical imbalances in the blood, such as potassium or calcium
- Problems breathing during sleep, known as obstructive sleep apnea
- Inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatic fever or lupus
What are the symptoms of bradycardia?
A heart rate that’s too slow can reduce blood flow to the brain. Symptoms of bradycardia include:
- Fatigue or feeling weak
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Confusion
- Fainting (or near-fainting)
- Shortness of breath
- Tiring easily during exercise
- Chest pain
What are complications of bradycardia?
Possible complications of bradycardia can include:
- Heart failure
- Frequent fainting (syncope)
- Cardiac arrest (in extreme cases)
How is bradycardia treated?
Borderline or occasional bradycardia may not need treatment.
Severe or prolonged bradycardia can be treated in a few ways. For instance, if a medication is causing a slow heart rate, the medication can be adjusted or stopped.
A pacemaker can often regulate the heart rate, speeding it up when needed.